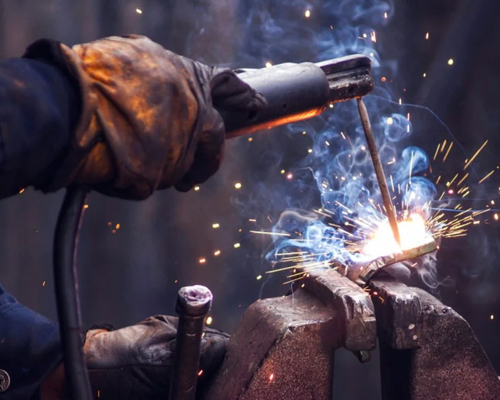
All Types of Welding
Welding is a fabrication process that lets you join materials like metals by using heat at high temperatures. Welding uses high temperature to join the materials, whereas soldering and brazing do not allow the base metal to melt. After cooling, the base metal and the filler metal get attached.
The welding process came to light when there was a search for the technique for developing iron into useful shapes. Welded blades were the first result of welding in the early years—the carburization of iron produced hard steel that was very brittle for usage. Later interlaying the rigid and soft iron with high-carbon material and hammer forging resulted in a tough and durable blade.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Welding
Advantages
- Welding establishes strong, durable, and permanent joint links.
- It is a simple process that results in a great finish.
- The technique, when used with filler material, produces a stronger weld than the base material.
- It can be performed at any place
- It is an economical and affordable process
- It is used in various sectors like construction, automobile, and many more industries.
Disadvantages
- It is hazardous when performed under the safety and security guidelines.
- It is a difficult task to dismantle the joined material through welding.
- Requires skilled labor and electric supply.